In the rapidly advancing world of manufacturing, resistance welding has carved out a crucial role as a leading method of metal joining. With over five decades of experience covering industrial technology, I can state confidently that resistance welding is not just another joining method—it is a cornerstone of modern fabrication processes. From automotive and aerospace to construction and consumer electronics, this welding continues to dominate due to its cost-effectiveness, speed, automation capability, and clean operation. This comprehensive guide explores what is resistance welding, its various types, applications, and how it compares to traditional welding techniques, all while highlighting essential supporting keywords such as electric resistance welding and flame resistance welding shirts.
What is Resistance Welding?
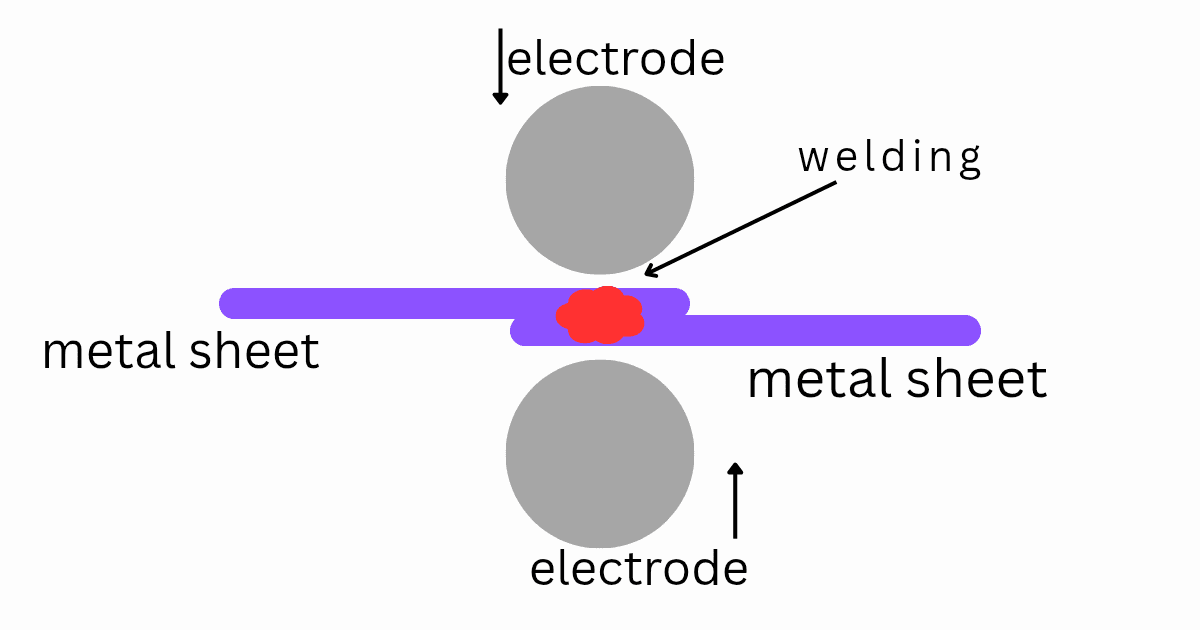
Resistance welding is a group of welding processes in which heat is generated by passing an electric current through the resistance caused by the contact between two or more metal surfaces. The generated heat, combined with pressure, is sufficient to form a weld. No filler materials, no open flames, and no complex shielding gases— just pure electrical resistance and pressure doing the job efficiently. This makes resistance welding clean, fast, and highly automated.
Types of Resistance Welding
Understanding this welding becomes easier when we examine its four most common subtypes:
- Spot Welding
In spot welding, electrodes clamp two metal sheets and pass current through them, creating welds at specific “spots.” This method is extensively used in automotive manufacturing—from car doors to structural components. - Seam Welding
Seam welding is a continuous welding process where rotating wheel electrodes produce an overlapping series of welds, forming a leak-tight seam. This is ideal for fuel tanks, transformers, and radiators. - Projection Welding
Used to weld multiple points simultaneously, projection welding utilizes a specially designed projection on one of the parts to concentrate the current flow, producing precise and uniform welds. - Flash and Upset Welding
These techniques involve pressing parts together while current is applied, allowing metal surfaces to fuse as resistance heats them. Common in rail joining and structural applications.
A key phrase you’ll encounter repeatedly in the industry is electric welding. As a subcategory of resistance welding, electric resistance type welding involves fusing materials using electric current with no need for flux or filler materials. Commonly used in pipe manufacturing, steel tubing, and structural shapes, electric resistance type welding has become a go-to for continuous, high-volume production lines. It is also divided into two primary types:
High-Frequency Electric Resist. Welding (HF-ERW)
Low-Frequency Electric Resist. Welding (LF-ERW)
Each variant offers a unique balance of penetration depth, weld strength, and material compatibility.

Advantages:
Why this welding method become the default solution in so many industries? The answer lies in its extensive list of advantages:
- Speed and Automation
Resistance welding processes are incredibly fast, making them ideal for high-volume operations. The process is easily automated, minimizing human error and increasing production speed. - Clean and Safe
There’s no arc, no sparks (except during initial contact), and no need for protective gas. This makes resistance type welding a safer alternative, particularly in clean manufacturing environments. - Energy-Efficient
Because heat is generated only at the interface, there is minimal energy wastage. Modern electric resistance welding machines are optimized for power efficiency. - Strong and Reliable Joints
This welding creates high-integrity welds that are both durable and consistent. It is especially effective for joining low-carbon steels and non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper.
Applications:
Today, the practical applications of said welding span multiple sectors:
Automotive Industry
The average modern car has over 5,000 spot welds, each made using resistance welding. From electric welding in car frames to robotic spot welders on assembly lines, this method ensures speed, uniformity, and strength.
Aerospace
In high-stress environments like aerospace, resistance welding is used to join thin gauge materials without compromising structural integrity. Construction and Infrastructure From bridge components to piping, electric resistance welding is used extensively in infrastructure development.
Electronics and Batteries
Miniature resistance welding machines are used in the assembly of circuit boards, battery packs, and micro-connectors.
Apparel Industry
While not commonly associated, flame welding shirts are a vital protective gear component in workplaces using resistance welding, ensuring worker safety from accidental sparks or overheating.
Flame Welding Shirts: A Crucial Safety Element
Welding safety gear is incomplete without mentioning flame resistance welding shirts. While resistance welding doesn’t produce an open flame like arc welding, the heat and occasional sparks still pose risks. These specialized flame welding shirts are:
- Made from fire-retardant materials like treated cotton or Nomex®
- Designed to withstand brief exposure to heat and sparks
- Essential in facilities using automated electric resistance welding machines
For safety managers and operators, incorporating flame resistance welding shirts as part of PPE protocols is non-negotiable.
What Sets Resistance Welding Apart?
The difference between this welding and other methods like MIG or TIG welding lies in its simplicity and efficiency. Here’s how it stands out:
| Feature | Resistance Welding | MIG/TIG Welding |
| Heat Source | Electrical Resistance | Electric Arc |
| Filler Material | Not Required | Required |
| Automation | High | Moderate |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Medium |
| Clean Operation | Yes | Requires Fume Extraction |
Limitations of Resistance type Welding
Despite its many benefits, resistance type welding isn’t a universal solution.
Here are a few challenges:
- Material Thickness Limits: Works best for thinner materials.
- Initial Cost: Equipment setup is capital intensive.
- Electrode Wear: Electrodes degrade with repeated use.
- Joint Design Restriction: Requires precise fit-up for optimal results.
However, innovations in resistance type welding and real-time quality monitoring are quickly overcoming these limitations.
Latest Innovations
The 2020-25 have seen a technological renaissance in this field
Adaptive Welding Systems
AI-driven systems adjust pressure, current, and weld time in real-time for optimized weld quality.
Robotic Integration
Automated arms equipped with resistance welding heads are now common in high-speed production lines.
Data Analytics in Electric Welding
Real-time data from sensors allows predictive maintenance, ensuring uninterrupted production cycles.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Unlike processes that release hazardous fumes, resistance type welding is a relatively clean process. With minimal consumables and low energy waste, it supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
It is an electrically powered, pressure-assisted joining process that excels in speed, efficiency, and repeatability. In today’s industrial climate, where production volume and consistency are paramount, resistance welding stands unrivaled. Whether through electric resistance type welding in steel mills, the adoption of flame welding shirts for safety, or answering the core question about welding, it’s clear that this technology is not just relevant—it’s indispensable.
Resistance welding is not a method of the past. It is the future, evolving rapidly with the help of robotics, AI, and smart materials. This blog has walked you through every essential facet— from technical nuances to safety and innovations—cementing this special type of welding as the go-to solution in global manufacturing.
Mule Robotics: Transforming Modern Construction with Intelligent Muscle in 2025
Robot Cart : Amazing Tool To Transform Industries In 2024.
Germanium Transistor: Loaded with Mesmerizing features for 21st century.
How do drone shows work? It’s Cost and technology behind this wonder.
What is the future of RPA developer? : Robotic Process Automation in 2025
RUST : BEST LANGUAGE FOR ROBOTICS in 2025?
10 Reasons Why I Love Robotics
Robot Wheel , Critical part of a robot in 21st century
The Future of AI: Top 7 Latest AI developments
What are the limitations of resistance welding?
Material thickness limit, higher cost, electrode wear are some disadvantages of resistance welding.
AC or DC which current does resistance welding use?
Mosty DC current is used in resistance welding. But as per requirement AC currents can also be used for some metals.
which type of electrode is used in resistance welding?
Class 2, like copper/chromium etc are used as a electrode, due to its low carbon high strength property.